Researchers in Switzerland have developed a variable stiffness catheter that can transition between soft and rigid states.
A team of researchers from technical university EPFL and ETH Zurich developed the catheter to make minimally invasive surgical interventions like cardiac arrhythmia treatment, simpler and more effective.
Catheters are inserted into arteries and navigated to treatment zones in many minimally invasive procedures. They can provide access to the heart without having to perform open-heart surgery. However, catheters can come with limitations.
Existing clinical magnetic catheters can only bend in one direction at a time.
“It would be helpful if some sections of the catheter could be very soft to freely bend and reach difficult areas, particularly in open volume operations,” Yegor Piskarev, a student at the university’s Laboratory of Intelligent Systems, said in a news release. “However, those same sections should also become rigid on command to enable precise control or achieve better pressure on the treatment zone.”
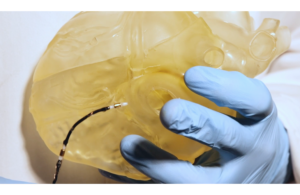
The EPFL and ETH team designed a catheter with flexibility and stiffness that can be adjusted during operations. It has two segments that allow the stiffness to change. Each segment has three layers: the innermost layer houses the cables needed to operate the catheter and cooling system; the central layer, made of conductive shape memory polymer, serves as a heater, temperature sensor and variable stiffness substrate; the outer layer, made of silicone, encapsulates the device.
“By selectively softening and stiffening individual segments, the catheter can better adapt to the body during navigation, and maintain the desired curvature when needed,” Dario Floreano, head of the Laboratory of Intelligent Systems, said.
The structure of the catheter makes it suitable for cardiac surgeries at just 2.3 mm in diameter, according to the researchers. The engineers fabricated it using a “dipping technique” to make the prototype.
Designed for remote magnetic navigation, the tip of the catheter has a small magnet that can be navigated through the body by an external magnetic field. Surgeons could then control the catheter’s movement with the help of a joystick. Manual catheters require X-rays to continuously monitor the catheter through a procedure, the researchers suggest.
“Remote magnetic navigation is a more recent and less common method, but appears to be more effective,” said Piskarev. “It prevents surgeons from being exposed to X-rays during imaging, and the joystick manipulation is simpler and quicker to learn.”
The researchers are still developing the device. The initial study was published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
